What is ESD Access Control System?
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Access Control System is a comprehensive security measure that integrates ESD testing, ESD turnstile and access control into a cohesive solution for EPA. This system is designed to grant entry privileges solely to employees who have passed their personal grounding device tests.
ESD Access Control System Overview Video
What is an ESD turnstile?
An ESD turnstile is a physical barrier integrated with ESD testing system designed to test the resistance of personnel grounding devices, ensuring that individuals entering an ESD protected area (EPA) are compliant with ESD safety standards. Furthermore, ESD turnstiles can incorporate access control mechanisms to strictly regulate entry into the area, thereby enhancing the overall ESD protection by preventing unauthorized access and ensuring that only personnel with proper grounding are allowed entry.
Types of ESD Turnstile
ESD turnstiles come in various forms to cater to different access control needs in high-security environments. Each type of ESD turnstile has its own unique features and benefits:
- ESD tripod turnstile: cost effective, one pass at a time, simple maintenance
- ESD flap barrier: high throughput, rubust and aesthetic design, no tailgating
- ESD swing barrier: wide pathway for moving materials, compact cabinet
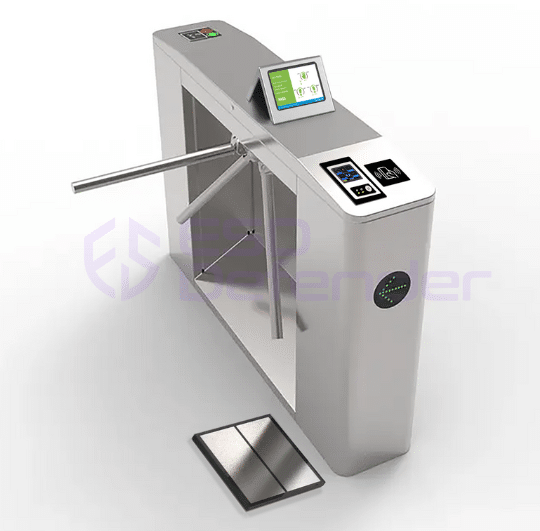
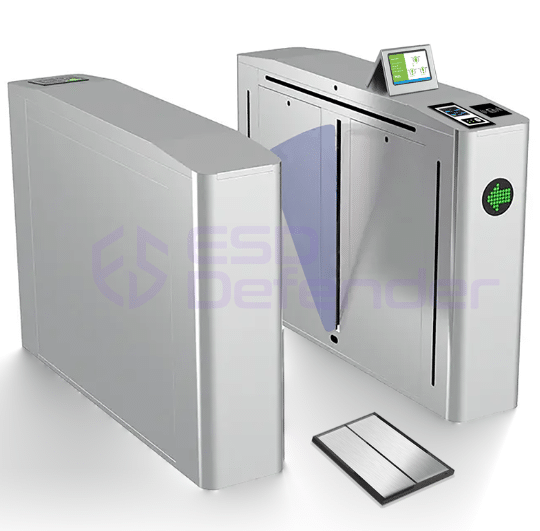
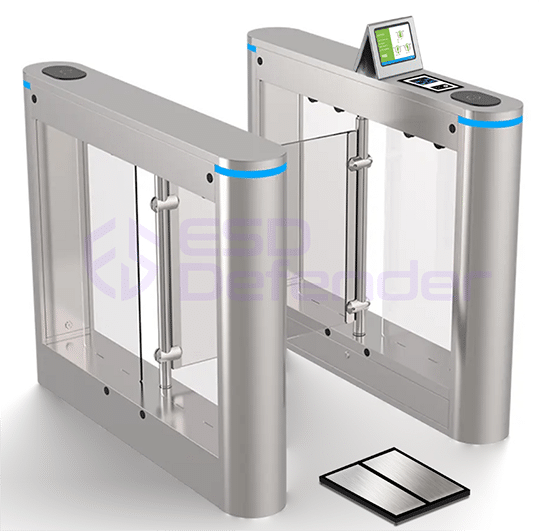



How much does ESD turnstile gate system cost?
As a general guideline, the typical cost range for an ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) turnstile gate system ccan be anywhere from $2,000 to $8,000. The cost of can vary depending on several factors, such as the specific features, add-ons, and vendor. Welcome to contact us for a quick quote.
Why EPA requires ESD Acess Control System rather than a single ESD Tester?
EPA is a designated workspace or environment designed to minimize the risk of electrostatic discharge-related damage to sensitive electronic components and devices.
Grounding is the simplest and most effective method for ESD control of conductive materials, including personnel grounding. Therefore, employees must wear ESD wrist straps, ESD grounders, or ESD footwear in EPA. However, the effective functioning of these devices cannot be determined by visual inspection alone.
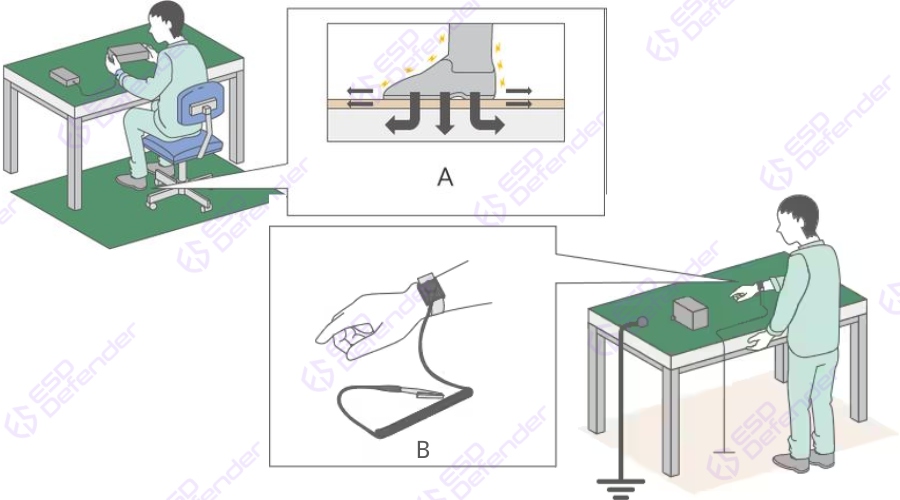
Limitations of using ESD tester without access control system
As a result, we require an ESD tester, which is a testing device used to evaluate the effectiveness of employee grounding equipment. However, using ESD tester only has the following limitations:
- Rely on manned monitoring-Empoyees may bypass the testing when not under direct supervision.
- Require for manual data recording- This may lead to protential for human error and inaccuracies
- Paper-based data storage-Maintaining paper-based test records impedes long-term tracking and corrective actions.
- Inability to prevent unauthorized personnel from entering the protected area.
Benefits of ESD access control system
The limitations of the traditional ESD tester highlight the need for a more advanced solution like the ESD Access Control System, which offers a range of key benefits to enhance EPA management:
- Automated Testing and Monitoring: The ESD Access Control System can automatically detect the ESD protective equipment worn by employees, eliminating the need for manual supervision and improving the continuity and reliability of the testing process.
- Real-Time Data Recording: The system can record each employee’s test data in real-time, avoiding the potential for errors associated with manual record-keeping.
- Digital Data Storage: The system utilizes an electronic database to store the test records, significantly improving the efficiency and security of data management.
- Historical Data Tracking: The system can maintain long-term test records, enabling analysis of trends and the implementation of timely corrective measures.
- Automatic Alerts: The system can immediately trigger alerts upon detecting any abnormal conditions, ensuring the safety of the EPA environment.
- Access Control: Integrated with ESD turnstile or electornic door lock, it can restrict unauthorized personnel from entering the EPA area, further strengthening the control of electrostatic discharge protection.
- Data Analysis: The system can generate various statistical reports, helping management personnel better understand the operational status of the EPA.
- Scalability: The ESD Access Control System has good scalability, allowing for flexible upgrades and adjustments based on evolving requirements.
- Improved Efficiency: The automated testing and monitoring significantly reduce the burden of manual management, thereby enhancing the overall operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: The use of this system can help organizations meet the relevant electrostatic discharge protection regulations, reducing compliance risks.
What is the principle of ESD control?
Understanding the generation of static electricity paves the way to grasping the principles of ESD control:
- Grounding of All Conductors, Including Personnel
- Removal of Unnecessary Non-Conductive Materials (Insulators)
- Using ESD Protective Packaging
- Humidity Control
Grounding of All Conductors, Including Personnel
Grounding prevents the accumulation of static charges on a conductor by providing a path for the charges to flow to the ground, thus neutralizing potential hazards.
- Ensure all personnel working in the ESD-sensitive area wear static-dissipative wrist straps that are properly grounded. ( Remember to utilize an ESD combo tester to assess the performance of both the wrist strap and footwear. )
- Require personnel to wear static-dissipative footwear or use conductive flooring to maintain a ground path.
- Ground all conductive surfaces, equipment, and fixtures using dedicated grounding systems.
Removal of Unnecessary Non-Conductive Materials (Insulators)
Insulating materials, or non-conductors, are prone to generating and retaining static charges. Without proper control, these materials can pose significant ESD risks.
- Replace non-conductive materials with static-dissipative or conductive alternatives, such as using ESD-safe tabletops, flooring, and shelving. Don’t forget to use surface resistivity meter to measure surface resistance and ensure materials meet ESD standards.
- Utilize ionizers to neutralize static charges on insulating surfaces and materials that can not be replaced.
- Maintain a minimum clearance between insulating materials and ESD-sensitive devices to minimize the risk of discharge.
Using ESD Protective Packaging
- Package ESD-sensitive devices in static-shielding bags, conductive containers, or other ESD-safe packaging before transportation and storage.
- Ensure the packaging provides a Faraday cage effect to distribute external static charges evenly on the outer surface, protecting the contents
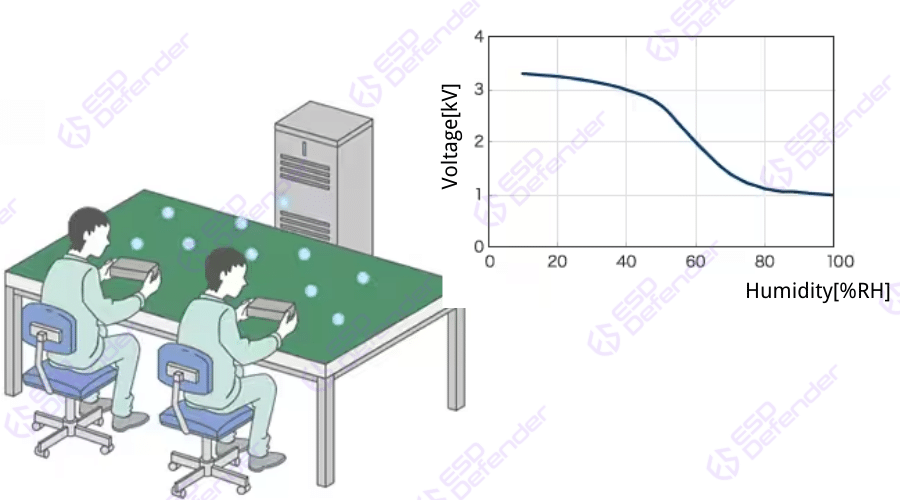
Humidity Control
The diagram below shows the natural discharge of static electricity as humidity increases. It is generally considered that when the relative humidity exceeds 65%, it is difficult for static electricity to be generated, and even if it is, it can be naturally dissipated. Therefore, this value is used as the benchmark for humidity management.
Why is ESD control important?
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) control is important for several reasons:
- Preventing Damage to Electronic Components: Electronic components, particularly sensitive semiconductor devices, can be easily damaged by static electricity. ESD can cause immediate failure or latent defects that lead to premature failure of the component. Proper ESD control measures help protect these sensitive components.
- Ensuring Product Reliability: Uncontrolled ESD can lead to intermittent failures or gradual degradation of electronic products over time. Implementing ESD control measures helps maintain the long-term reliability and performance of electronic devices.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries, such as electronics manufacturing, have established ESD control standards and guidelines that must be followed to ensure product quality and safety. Adhering to these standards is often a legal requirement.
- Reducing Warranty and Repair Costs: ESD-related failures can lead to increased warranty claims and product returns, which can be costly for manufacturers. Effective ESD control helps minimize these expenses.
- Protecting Personnel: Static electricity can also pose a safety risk to personnel, as it can cause shocks or even ignite flammable materials. ESD control measures help protect workers from these hazards.
Overall, ESD control is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of electronic products, ensuring compliance with industry regulations, and protecting both equipment and personnel from the harmful effects of static electricity.
Major Sources of Electrostatic Discharge in the Electronics Industry
The electronics industry is a high-risk area for electrostatic discharge (ESD). During the various manufacturing and assembly processes of electronic devices, such as testing, soldering, heating, drying, cleaning, inspection, handling, packaging, and transportation, the components inevitably experience collisions and frictional contact, which can generate high electrostatic potentials. Furthermore, if the operator is charged for any reason and does not implement reliable anti-static measures, the electrostatic potential of the human body can reach as high as 1.5-35 kV, which can also lead to damage or soft breakdown of the electronic devices.
In fact, the human body and the electronic devices themselves are significant sources of static electricity. Charged human bodies and charged devices both constitute ESD sources that pose a threat to the electronic components. There are also other static electricity sources in the environment surrounding the electronic devices, such as work-related static and packaging materials.
| Workbench Surfaces | – Waxed, painted, or lacquered surfaces – Regular vinyl materials – Various plastics |
| Flooring | – Sealed concrete – Waxed or painted wood flooring – Regular vinyl tiles or sheets |
| Clothing | – General clean room garments – Typical synthetic fiber work clothes – Regular shoes – Dry cotton (below 30% RH) |
| Chairs | – Vinyl chairs – Fiberglass chairs – Painted wooden chairs |
| Packaging and Handling | – General plastics (bags, cases, envelopes) – Regular bubble wrap, foam materials – General plastic trays, totes, transport boxes, vials – Component storage containers |
| Assembly, Cleaning, Testing, Repair Areas | – Spray cleaning equipment – Regular desoldering tools – Ungrounded soldering irons – Brushes (synthetic bristles) – Liquid or evaporative cleaning/drying – Low-temperature spray guns or hot air guns – Sandblasting – Electrostatic copying |
| Chip Carriers | – Chip trays and racks – Magazines – Tools |
| Logistics Equipment | – Storage cabinets – Handling carts |
| High Voltage Equipment or Sources | – Various metal parts, components, and equipment that can induce static electricity |
How to use ESD check station?
ESD check station, also called ESD test station, is a specialized workstation designed to measure and control electrostatic discharge (ESD) in electronic manufacturing and assembly environments. To use an ESD check station, begin by ensuring that all personnel are wearing appropriate ESD protection gear, such as wrist straps or ankle straps, which are grounded to prevent static buildup.
Additionally, it is essential to utilize a surface resistance meter to measure the resistance of various materials that will be used in ESD-sensitive work areas. This measurement helps ensure that the surfaces and tools maintain proper conductivity, further reducing the risk of ESD and protecting sensitive electronic components.
