What is a shoe sole cleaner machine?
A shoe sole cleaning machine is a device equipped with rotating brushes or moving tracks that automatically scrubs dirt and debris. Shoe sole cleaner machines are commonly used in high-contamination-risk environments (e.g., farms, food processing plants) and particle-sensitive facilities (e.g., electronics factories, chip manufacturing facilities, cleanrooms).
Core Parts of a Shoe Sole Cleaner Machine
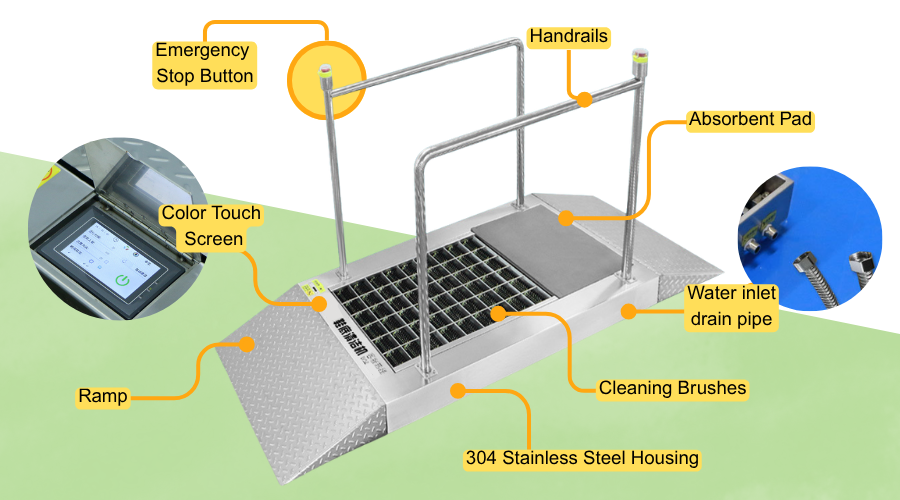
Understanding the essential components is key to choosing the right machine. Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental parts found in most models:
Sturdy Housing:
Material: Typically 304 stainless steel for durability, hygiene and corrosion resistance.
Drive Motor:
Function: Powers the cleaning mechanism (brushes or belt).
Control Panel:
Interface: Touchscreen displays for easier operation and settings adjustment (e.g., people counts, cycle time).
Cleaning Brushes/Belt:
Material: high-quality DuPont bristles for effective scrubbing and longevity
Water Management System:
Application: Dispenses water/cleaner onto brushes/belt.
Recovery: Includes an absorbent pad at the exit to capture excess water.
Drainage: Features an automatic drainage tank to collect wastewater for easy disposal.
Safety & Support:
Access Ramp: Often includes an integrated ramp (typically 304 stainless steel with anti-slip texture) for easy and safe stepping onto the cleaning platform.
Support/Safety Options: May include handrails for stability and an emergency stop button for immediate shutdown.
How Does a Shoe Sole Cleaner Machine Work?
Shoe Sole Cleaner Machines are essential in cleanrooms, electronics manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceutical facilities. They prevent external contaminants from entering controlled environments via footwear. Here’s a streamlined breakdown of their operation:
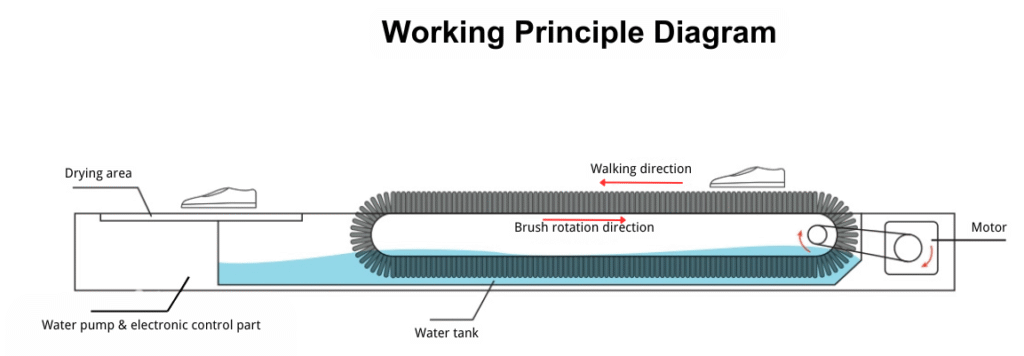
- Controlled Brushing Action
- A pressure or motion sensor activates the machine when stepped on.
- Electric motors spin water- or cleaning-solution-soaked roller brushes (nylon/PVC).
- Brush tips scrub shoe soles vertically/horizontally, dislodging particles through friction.
- Contaminant Removal
- Dislodged debris (dust, soil, microbes) falls onto a rotating scraper belt beneath the brushes.
- This belt sweeps contaminants into a wastewater tank, preventing reattachment.
- Automated Water Management
- Drain Phase:
Timers/sensors trigger solenoid valves to drain dirty water into facility wastewater pipes. - Refill Phase:
Clean water (filtered/DI water) refills the tank to a preset level via float switches/sensors.
- Drain Phase:
Where Shoe Sole Cleaner Machines Are Essential?
Shoe sole clean machines are critical in environments where microscopic contaminants threaten safety, quality, or functionality:
- Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing
- A single ≥0.5µm particle can ruin microchips. Machines remove 99%+ particles from soles to protect wafer fabrication (ISO Class 1-5 cleanrooms).
- Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology Labs
- Prevent microbes/particles from compromising sterile drug production (GMP compliance) or cell cultures. Critical in vaccine/API manufacturing.
- Medical Device Assembly & Hospitals (Surgical Suites)
- Eliminate pathogens (e.g., C. difficile) and dust that could infect patients or contaminate implants.
- Food & Beverage Processing Plants
- Stop soil/pathogens (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli) from footwear entering production lines (HACCP/FSSC 22000 requirements).
- Aerospace & Precision Optics
- Dust or fibers on shoe soles can degrade satellite sensors/laser optics during assembly.
- Research Cleanrooms (Nanotech, Physics Labs)
- Maintain “particle-free” conditions for experiments (e.g., quantum computing).
Types of Sole Cleaner Machines
Imagine shoe soles as disease vectors (hospitals), static bombs (cleanrooms), or toxin carriers (labs). Procuring sole cleaners is non-negotiable for contamination control. Before investing, it is important to know: What types of sole cleaner machines exist?
Grouped by brush mechanism, sole cleaners fall into two types: Rotating Brush and Belt Brush systems. This defines the core mechanical action used to scrub soles.
| ▶ By Brush Mechanism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Picture |  |  |
| Brush | Roller Brush(Rotating Cylinders) | Belt Brush(Moving Brush Matrix) |
| Best for | • Safety boots • Oil-resistant work boots • Mud-covered hiking shoes | • ESD shoes/flat soles • Cleanroom booties • Medical clogs |
| how it works | 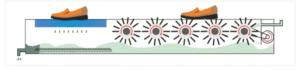 | 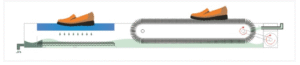 |
| Avaliable Length | 1.0/1.3/1.5/1.8/2.0/2.3/2.8/3.0 meter | |
| Read More | Read More | |
Grouped by cleaning method, the key types are Water Wash and Dry Brush systems. This determines the required infrastructure and maintenance.
| ▶ By Cleaning Method | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Wet-Wash Systems | Dry-Brush Systems |
| How It Works | • Auto-fills water/cleaning solution • Uses absorbent rollers to lift dissolved dirt • Auto-drains wastewater | • Motorized brushes dislodge dry debris • Integrated high-suction vacuum (≥20 kPa) captures dust • Requires dust filtration bags |
| Best For | Environments needing deep cleaning: - Food processing plants (grease, organic residue) - Pharmaceutical labs (sticky contaminants) - Rain/snow entry zones (mud, deicing salts) | Low-moisture areas: - Electronics cleanrooms (static-sensitive dust) - Precision workshops (abrasive particles) Note: Higher noise levels (65–75 dB) |
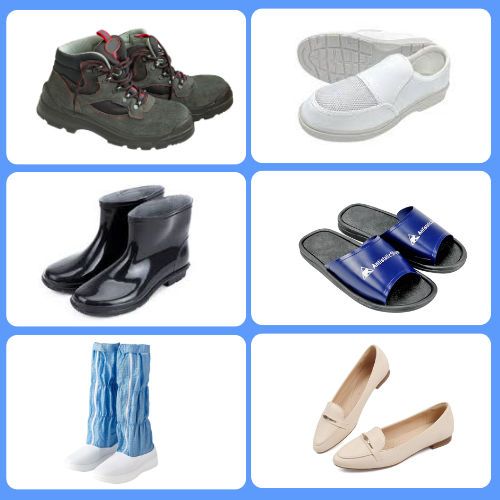
What Types of Shoe Soles & Debris Can Be Removed?
Shoe sole cleaning machines work effectively on soles with both shallow treads and deep treads.. They effectively handle a wide range of footwear types commonly found in various work and entry environments, including:
- Cleanroom Shoes & Booties
- ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Shoes
- Cleanroom Boots
- Safety Boots & Work Boots
- Athletic Shoes / Sneakers
- Women’s Flats & Loafers
- Rain Boots
- and more…
Note: No High Heel Shoes

Shoe sole cleaning machine is designed to remove debris carried on the soles, typically includes:
- Particulate Matter: Dust, dirt, soil, sand, grit.
- Organic Debris: Grass clippings, leaves, food particles (especially relevant in food processing).
- Industrial Residues: Metal shavings, plastic pellets, light oils, or greases (depending on machine design and cleaning solutions used).
- Salt/Chemical Residues: Tracked in from winter roads or specific industrial processes
Shoe sole cleaning machine handles diverse soles through its combination of multiple cleaning modules (using varied brush types and designs) and adjustable settings for parameters like cleaning time and intensity. These elements work together to tailor the cleaning process precisely to the footwear’s specific characteristics and requirements.
How Much Does A Footwear Cleaning Machine Cost?
Footwear sole cleaning machine generally costs between $1,500 and $3,500 USD. The final price depends on factors such as the material, size, performance, and level of intelligence of the equipment.
As a manufacturer, we want you to understand that these price differences stem from both visible and invisible “hard costs”:
“Skin” – Material Costs: Whether a machine is built from ordinary steel or fully from 304 stainless steel makes a difference of several times in both raw material and processing costs. This directly determines the machine’s ability to withstand day-after-day exposure to humid environments and chemical corrosion—whether it becomes rust-covered in 3 years or remains as solid as new for a decade.
“Heart” – Power System: The quality of the motor is core to the machine’s long-term stable operation. There is a vast gap in noise, power consumption, heat generation, and lifespan between cheap aluminum-wire or standard motors and national-standard pure copper wire motors or branded frequency conversion motors. This impacts future maintenance costs and the risk of operational downtime.
“Hands” – Cleaning System: The number of brushes, their layers, and their material are a direct reflection of the cleaning effectiveness. Three layers of brushes will undoubtedly clean more thoroughly than a single layer. High-quality nylon/PVC hybrid brushes are wear-resistant and won’t damage floors, but their cost is significantly higher than that of ordinary brush filaments.
“Brain” – Intelligent Control: From a simple manual switch, to infrared sensor auto start-stop, all the way up to PLC intelligent control systems with self-diagnostic capabilities—each step up in automation level signifies an increase in component and R&D costs. However, it also brings energy savings, convenience, and significantly enhanced reliability.
Effective Maintenance For Automatic Shoe Sole Cleaning Machine
Regular maintenance is the key to ensuring your machine has a long, effective life. A well-maintained cleaner won’t just work better; it will also prevent unpleasant odors and potential breakdowns.
- Clean the absorbent mat daily or every few days, depending on frequency of use.
- Manually remove hair and debris scattered on the rollers.
- Open the water tank and manually take out large objects, such as Anti-static finger cots or stones.
- Click “Manual Drain” on the display screen to discharge dirty water.
- Use the provided brush to remove deposited fine dust and sludge along with the dirty water.
- Clean the mud on the water level sensor promptly if present.
Pro Tip: Always remember to turn off and unplug the machine before performing any manual cleaning inside the tank for safety.
